|
Optimal Extraction Sequence (OES)
An Optimal Extraction
Sequence for an Ultimate Pit
Optimal Extraction Sequences (OES) are generated by Pit Optimizer, PB Generator, Scheduler and MFO.
The OES is the extraction sequence for all blocks in the model which provides the highest possible NPV for a logically possible sequence of mining. Within Studio NPVS, an OES is calculated at each stage of processing.
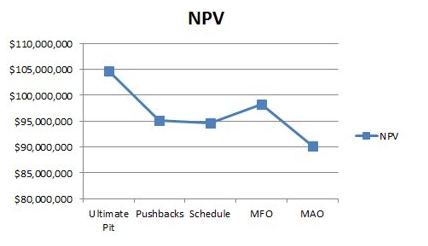
As designs and schedules are modified to be more realistic the NPV of a project tends to decrease:
Their Purpose
● Information transfer between optimization programs.
● Uniform and intuitive means of presenting optimization results.
● To provide consistency for NPV calculations, reporting and surface generation.
● To assist in the ultimate goal of achieving maximum NPV.
Principles
● Follow pit by pit (LG shell, pushback, annual pit) rule.
● Within a pit, follow bench by bench rule.
● Follow the contiguous mining rule whenever possible.
● Extract higher value blocks before lower value blocks.
Pit Optimizer’s blending OES is an exception; it ignores the above rules focusing solely on meeting blending targets.
What is an OES?
-
A physically mineable sequence of model blocks.
-
Practically mineable depending on:
-
-
The type of the project; a Pit Optimizer OES may be practical for a small talk mine but is unlikely to be practical for a large copper mine.
-
The optimization stage; for most mines only Scheduler and MFO sequences can be considered practical.
-
-
Optimal in the sense that we can be fairly confident to get higher NPV by mining most of the blocks labeled '1' to '100' before the blocks labeled '101' '200'.
-
The best guess at mining strategy prior to medium and short term scheduling.
OES Limitations
● OES is not optimal in detail; for example, it does not guarantee that mining block 55 before block 56 will result in higher NPV.
● In cases when LG parameterization logic fails to deliver maximum NPV (these cases can sometimes be predicted), Pit Optimizer OES will not be optimal in the aggregate sense either †.
† General NPV maximization problem is intractable for real mines. The methods that solve this problem are applicable to academic examples with less than 100,000 blocks and uniform slopes, and even then the computation time is counted in days.
|
|
Related Topics |
|
|
Pit Optimization
Essentials |
Copyright © Datamine Corporate Limited
JMN 20065_01_EN